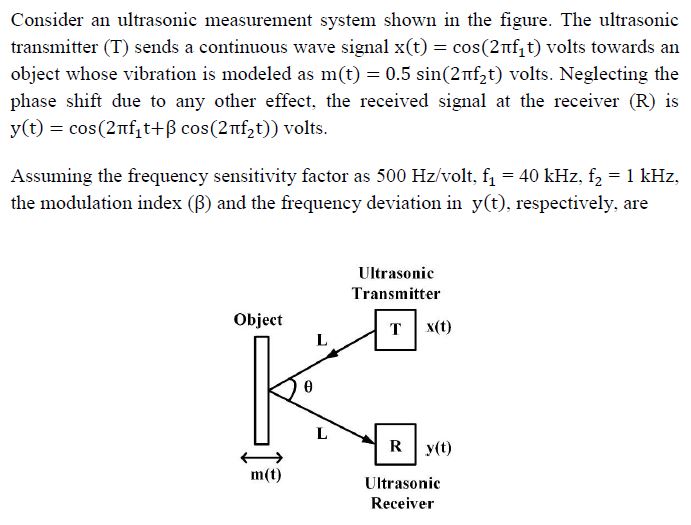
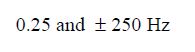
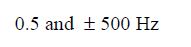
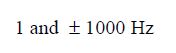
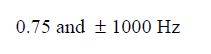
Consider an ultrasonic measurement system shown in the figure. The ultrasonic transmitter $(T)$ sends a continuous wave signal $x(t)=\cos \left(2 \pi f_{1} t\right)$ volts towards an object whose vibration is modeled as $m(t)=0.5 \sin \left(2 \pi f_{2} t\right)$ volts. Neglecting the phase shift due to any other effect, the received signal at the receiver (R) is $y(t)=\cos \left(2 \pi f_{1} t+\beta \cos \left(2 \pi f_{2} t\right)\right)$ volts.
Assuming the frequency sensitivity factor as $500 \mathrm{~Hz} /$ volt, $\mathrm{f}_{1}=40 \mathrm{kHz}, \mathrm{f}_{2}=1 \mathrm{kHz}$, the modulation index $(\beta)$ and the frequency deviation in $y(t)$, respectively, are
0.25 and $\pm 250 \mathrm{~Hz}$
0.5 and $\pm 500 \mathrm{~Hz}$
1 and $\pm 1000 \mathrm{~Hz}$
0.75 and $\pm 1000 \mathrm{~Hz}$